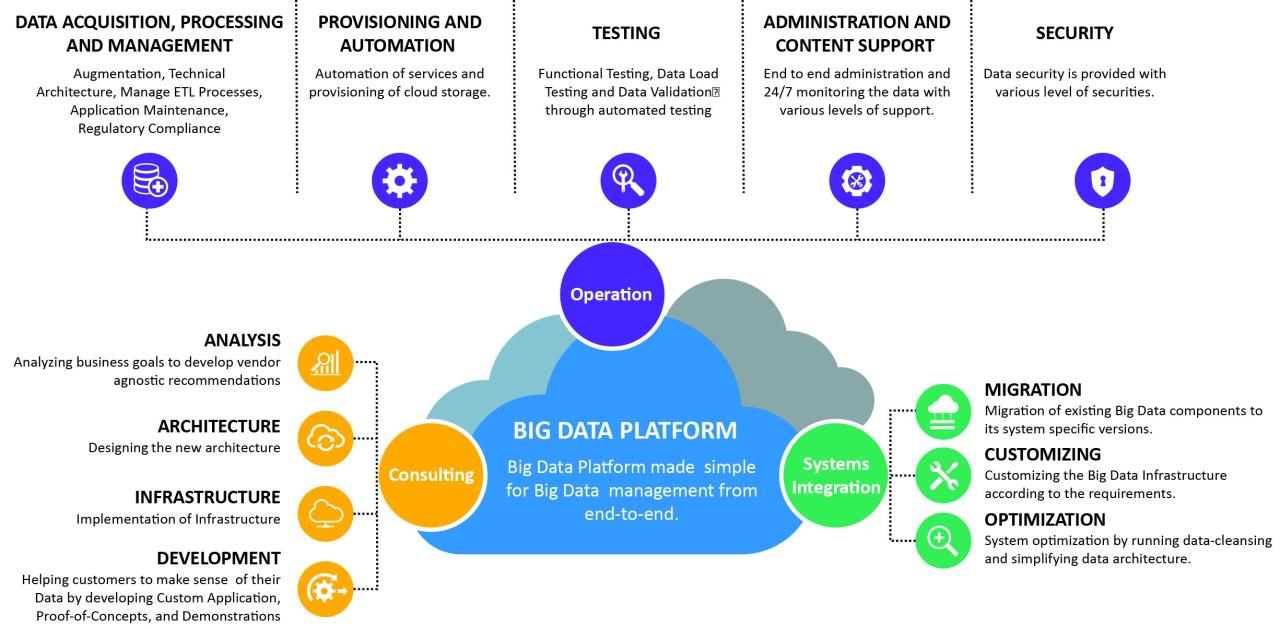
Definition of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting electronic systems, networks, and data from malicious attacks and unauthorized access. It involves the use of various security measures to prevent, detect, and respond to threats that compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information.
Cybersecurity threats come in various forms, including:
- Malware:Malicious software designed to damage or steal data, such as viruses, worms, and ransomware.
- Phishing:Fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information by impersonating legitimate organizations or individuals.
- Hacking:Unauthorized access to computer systems or networks with malicious intent.
- Social engineering:Exploiting human vulnerabilities to gain access to sensitive information or systems.
- DDoS attacks:Distributed denial-of-service attacks that overwhelm a system with excessive traffic, rendering it inaccessible.
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities arise from weaknesses in systems or software that can be exploited by attackers to gain access or compromise data. Common vulnerabilities include:
- Weak passwords:Passwords that are easy to guess or crack.
- Unpatched software:Software that has not been updated with the latest security patches, leaving it vulnerable to known exploits.
- Unprotected networks:Networks that lack adequate security measures, such as firewalls or intrusion detection systems.
- Misconfigured systems:Systems that have not been properly configured, leaving them open to exploitation.
- Insider threats:Malicious or negligent actions by authorized users who have access to sensitive data.
Importance of Cybersecurity

In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, cybersecurity has emerged as an indispensable pillar, safeguarding the integrity and confidentiality of our increasingly interconnected world. Its critical importance stems from the pivotal role it plays in protecting sensitive information, securing critical infrastructure, and ensuring business continuity in the face of ever-evolving cyber threats.
Protection of Sensitive Information
Cybersecurity measures are essential for safeguarding sensitive personal and financial data, such as passwords, credit card numbers, and medical records. With the proliferation of online transactions and the rise of data breaches, robust cybersecurity practices are crucial to prevent unauthorized access and protect individuals from identity theft, financial loss, and other privacy concerns.
Cybersecurity Best Practices
Cybersecurity best practices encompass a comprehensive set of measures that individuals and organizations can implement to protect their digital assets and mitigate cybersecurity risks. These practices include, but are not limited to, strong password management, software updates, and security awareness training.
Password Management
Effective password management is crucial for preventing unauthorized access to sensitive accounts. Best practices include creating strong passwords, avoiding password reuse, and enabling two-factor authentication.
- Create strong passwords:Use a combination of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Avoid password reuse:Use different passwords for different accounts to minimize the impact of a password breach.
- Enable two-factor authentication:Require a second form of authentication, such as a code sent to your phone, when logging into sensitive accounts.
Software Updates
Regularly updating software patches and security updates is essential for addressing vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
- Install software updates promptly:Apply software updates as soon as they become available.
- Enable automatic updates:Configure your devices and software to automatically install updates.
- Use reputable software sources:Download software only from trusted sources to avoid malware infections.
Security Awareness Training, Cybersecurity
Security awareness training educates users on cybersecurity risks and best practices, empowering them to make informed decisions and avoid common threats.
- Provide regular training:Conduct security awareness training sessions for employees and individuals.
- Use engaging content:Make training interactive and engaging to increase retention.
- Cover common threats:Include topics such as phishing, malware, and social engineering.
Cybersecurity Threats and Countermeasures

Cybersecurity threats pose significant risks to individuals, businesses, and organizations. Understanding these threats and implementing effective countermeasures is crucial for maintaining data integrity, privacy, and overall security.
Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, is a type of software designed to harm or disrupt a computer system. It can include viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware. Malware can spread through email attachments, malicious websites, or infected USB drives.
- Consequences:Malware can steal personal information, corrupt data, damage software, or disrupt network operations.
- Countermeasures:Install antivirus software, keep software updated, be cautious when opening email attachments, and use firewalls.
Phishing
Phishing is a type of cyberattack that attempts to trick users into providing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card numbers. Phishing emails or websites often impersonate legitimate organizations and contain links to malicious websites.
- Consequences:Phishing can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and data breaches.
- Countermeasures:Be cautious when clicking links in emails or on websites, check the sender’s email address, and never share personal information via email.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts files and demands payment to decrypt them. It can target both individuals and businesses, causing significant financial losses and disruption.
- Consequences:Ransomware can render files inaccessible, disrupt operations, and lead to financial extortion.
- Countermeasures:Regularly back up data, install antivirus software, keep software updated, and be cautious when opening email attachments.